爱语导读:科学家首次掌握证据,表明南极上空巨大的臭氧空洞开始逐渐修复。
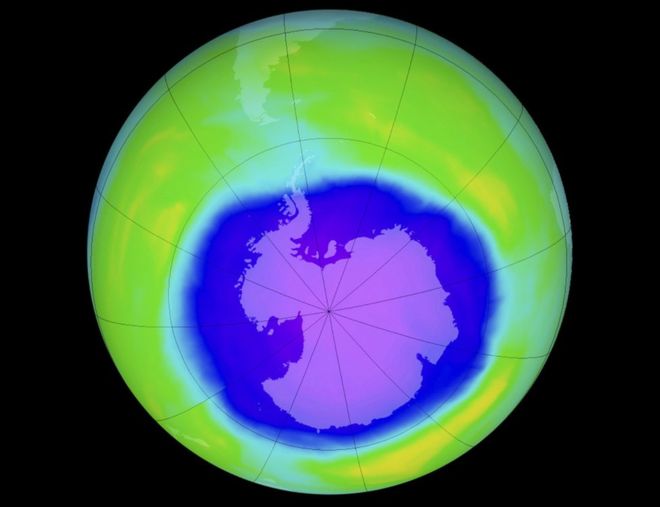
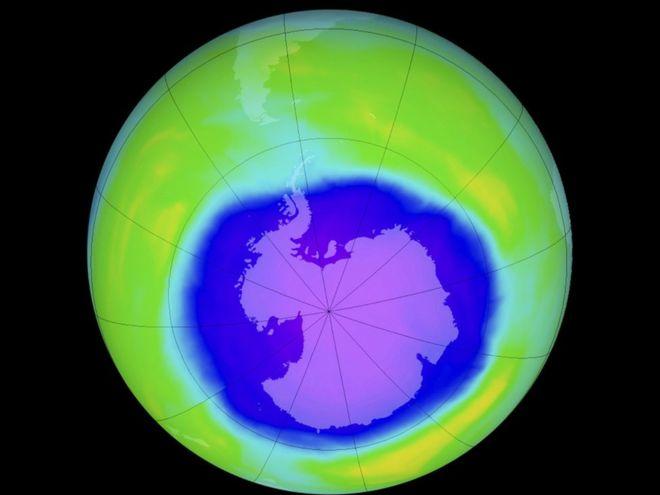
Researchers say they have found the first clear evidence that the thinning in the ozone layer above Antarctica is starting to heal.
研究者称他们找到首个清晰证据,能够证明南极洲上空臭氧层变薄的现象已开始自我修复。
The scientists said that in September 2015 the hole was around 4 million sq km smaller than it was in the year 2000 - an area roughly the size of India.
科学家称,2015年9月臭氧层空洞面积比2000年小了400万平方千米-约为整个印度的国土面积。
The gains have been credited to the long term phasing out of ozone-destroying chemicals.
自我修复源于人类长期禁止使用破坏臭氧层的化学物质。
The study also sheds new light on the role of volcanoes in making the problem worse.
该研究同时阐明了火山在臭氧层空洞问题上不可忽视的影响。
Skin cancer worry
皮肤癌的担忧
British scientists first noticed a dramatic thinning of ozone in the stratosphere some 10 kilometres above Antarctica in the mid 1980s.
英国科学家在上世纪80年代首先注意到,在南极洲上空10km左右的平流层中出现了臭氧层急剧变薄的现象。
Ozone is important because it blocks out harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
臭氧层很重要,因为它能阻挡太阳紫外线的伤害。
Its absence increases the chances of skin cancer, cataract damage, and harm to animals and plants.
臭氧层缺失会增加皮肤癌和白内障的风险,而且会对动植物产生危害。

In 1986, US researcher Susan Solomon showed that ozone was being destroyed by the presence of molecules containing chlorine and bromine that came from chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). These gases were found in everything from hairsprays to refrigerators to air conditioning units.
1986年,美国研究者Susan Solomon证明,臭氧的破坏是由含有氯和溴的分子造成,这些分子来源于氯氟烃(CFCs),它广泛存在于喷发剂、冰箱以及空调机组中。
The reason the thinning was occurring mainly over Antarctica was because of the extreme cold and large amounts of light. These helped produce what are termed Polar Stratospheric Clouds.
臭氧层变薄主要发生在南极洲上空,因为这里有极寒的气候以及大量光照,而这些有助于所谓“极地平流层云”的形成。
In these chilled-out clouds, the chlorine chemistry occurs that destroys the ozone.
在这些寒冷的云层中,氯生成并开始破坏臭氧层。
Thanks to the global ban on the use of CFCs in the Montreal Protocol in 1987, the situation in Antarctica has been slowly improving.
多亏了1987年《蒙特利尔议定书》禁止使用氯氟烃,南极洲上空的状况渐渐缓慢改善。
Several studies have shown the declining influence of CFCs, but according to the authors this new study shows the "first fingerprints of healing" and the ozone layer is actively growing again.
许多研究已经证明氯氟烃的影响在减小,但据作者称,这项新研究证明了“愈合的第一个印记”,并且臭氧层已经再次自我“生长”。
Prof Solomon and colleagues carried out detailed measurements of the amount of ozone in the stratosphere between 2000 and 2015.
Solomon教授和同事在2000年到2015年间展开了臭氧含量的详细测量。
Using data from weather balloons, satellites and model simulations, they were able to show that the thinning of the layer had declined by 4 million sq km over the period. They found that more than half the shrinkage was due solely to the reduction in atmospheric chlorine.
通过气象气球、卫星和模型模拟等数据,他们能够证明这段时期内臭氧层变薄区域减少了400万平方千米。他们发现超过半数减小区域是由于大气氯的减少导致。
Normally measurements are taken in October when the ozone hole is at its largest. But this team believed they would get a better picture by looking at readings taken in September, when temperatures are still low but other factors that can influence the amount of ozone, such as the weather, are less prevalent.
测量通常情况下会在十月份进行,这时臭氧层空洞最大。然而该研究小组认为在九月份测得的读数能够看的更清晰,因为这时候温度仍然很低,但其他影响臭氧含量的因素(如天气)影响较小。
"Even though we phased out the production of CFCs in all countries including India and China around the year 2000, there’s still a lot of chlorine left in the atmosphere," Prof Solomon told the BBC World Service Science in Action programme.
“尽管我们在2000年就在所有国家(包括印度和中国)停止生产氯氟烃,但大气层中仍有很多氯的残留物。”Solomon教授在行动计划中告诉BBC全球科学服务栏目。
"It has a lifetime of about 50-100 years, so it is starting to slowly decay and the ozone will slowly recover.
“它的寿命大概有50-100年,所以它已经开始逐渐衰退,而臭氧将慢慢恢复。”
"We don’t expect to see a complete recovery until about 2050 or 2060 but we are starting to see that in September the ozone hole is not as bad as it used to be."
“预计到2050年或2060年才能完全恢复,但我们已经看到,九月份臭氧空洞已经不如以前那么糟糕了。”
One finding that puzzled researchers was the October 2015 reading that showed the biggest ozone hole on record over Antarctica.
有一项发现令研究者们感到困惑:2015年10月份的读数显示,南极洲出现了有史以来最大的臭氧空洞。
The scientists believe that a key contributor to the record hole was volcanic activity.
科学家们认为主要原因是火山活动。
"After an eruption, volcanic sulphur forms tiny particles and those are the seeds for Polar Stratospheric Clouds," Prof Solomon told Science in Action.
“火山喷发后,火山硫黄会形成小颗粒,这些小颗粒是极地平流层云的种子。”Solomon教授告诉《科学在行动中》栏目。
"You get even more of these clouds when you have a recent major volcanic eruption and that leads to additional ozone loss."
”当近期有大型火山喷发,这些云层会增多,从而导致额外的臭氧损失。”
"Until we did our recent work no-one realised that the Calbuco eruption in Chile, actually had significantly affected the ozone loss in October of last year."
“完成近期工作之前,没人意识到智利卡尔布科火山喷发实际对去年10月份的臭氧损失有着重大影响。”
The study has been hailed as "historically significant" by some other researchers in the field.
该研究被同行业内其他研究者奉为“具有历史意义的重大事件”。
"This is the first convincing evidence that the healing of the Antarctic ozone hole has now started," said Dr Markus Rex from the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research in Germany.
“这是第一个有说服力的证据,表明南极洲臭氧空洞现在已经开始愈合。”德国极地与海洋研究中心阿尔弗雷德韦格纳研究所的Markus Rex博士说。
"Right now the state of the ozone layer is still really bad, but I find it very important that we know the Montreal Protocol is working and has an effect on the size of the hole and that is a big step forward."
“现在臭氧层的状况仍然十分糟糕,但是我们知道《蒙特利尔议定书》起作用了并且对臭氧层空洞大小有影响,这点非常重要,我们也因此前进了一大步。”
Differing views
不同意见
However others are not entirely convinced that the decline shown in the new study is down to a reduction in the amount of chlorine in the stratosphere.
然而对于新研究中提出臭氧空洞缩小是由于平流层中氯含量降低这一观点,一些人并未完全信服。
"The data clearly show significant year to year variations that are much greater than the inferred trends shown in the paper," said Dr Paul Newman from Nasa.
“数据清晰表明,年际变化比论文中推断出的趋势大的多。”来自美国国家宇航局的Paul Newman博士说。
"If the paper included this past year, which had a much more significant ozone hole due to lower wave driven forcing, the overall trend would be less."
“如果论文包括去年的数据(去年由于低波驱动力,臭氧层空洞大得多),那么总体变化趋势会更小。”
Regardless of these questions, the scientists involved in the study believe the ozone story is a great role model for how to tackle global environmental problems.
尽管有许多质疑,参与此项研究的科学家们认为,臭氧层变化的案例为解决全球环境问题树立了一个好的榜样。
"It’s just been remarkable," said Prof Solomon.
“这真是了不起。”Solomon教授说。
"This was an era in which international co-operation went rather well on some issues. I was inspired by the way the developed and developing countries were able to work together on dealing with the ozone hole," said Prof Solomon.
“在这个年代,国际合作在某些问题上做得非常好。发达国家和发展中国家合作解决臭氧层空洞问题的方式给了我很大启发。”Solomon教授说。
完成阅读
来源:BBC
【对于学习,从现在开始,你还没有晚。别说自己没基础,慢慢来;你不懂?问我吧!——订阅微信公众号:爱语吧VOA(iyubavoa】

 )
)






























我来说两句排行榜